Want to extend the life of your garage door, prevent costly repairs, or maybe even tackle some DIY maintenance? It all starts with understanding the parts that make it work.
This essential guide provides a clear overview of a garage door’s anatomy, explaining the role of each component and offering valuable insights for homeowners. Get ready to become a garage door expert!
Main sections of a garage door
Before we discuss individual components, it’s helpful to understand the basic structure of a garage door. Each section plays a crucial role in the overall performance and longevity of the door. Let’s break it down.
1. Door sections
The most visible part of your garage door is the door itself! These are typically composed of individual panels or sections joined together. This sectional construction allows the door to bend and curve along the track as it opens and closes.
Now, you’ll find these sections come in a variety of materials, each with its own pros and cons:
- Steel: A popular choice for its durability, affordability, and low maintenance. You can find steel doors in various gauges (thicknesses) and with different finishes for added protection against the elements.
- Wood: Offers a classic, warm aesthetic appeal. Wood doors can be customized with different stains and paints to match your home’s style. However, they require regular maintenance to prevent rot and warping.
- Aluminum: Aluminum doors are lightweight and resistant to rust, making them a good option for coastal areas. They are often modern and can be insulated for improved energy efficiency.
- Fiberglass: Durable and resistant to dents and cracks. Fiberglass can mimic the look of wood without the maintenance headaches, but it can be more expensive.

Canyon Ridge
Brick
Robyn Morrow Home
Insulation and R-Value
Consider insulated sections if you’re looking for a garage door that helps regulate temperature and reduce energy costs. Insulation is typically made from polystyrene or polyurethane foam sandwiched between the layers of the door material.
The effectiveness of insulation is measured by its R-value, which indicates its resistance to heat flow. Higher R-values mean better insulation. Remember that your garage door’s R-value should be chosen based on your local climate and how you use your garage.
2. Hardware
Think of the hardware as your garage door system’s connective tissue and joints. These essential pieces work together to guide, support, and move the door sections along the tracks.
Hinges

Hinges are like the elbows of your garage door, allowing the sections to bend and fold as the door opens and closes. They’re typically made of galvanized steel for strength and corrosion resistance. You’ll find different types of hinges depending on their location on the door:
- End hinges: Connect the sections at the edges of the door.
- Center hinges: Join the sections in the middle.
- Top and bottom hinges: Attach the door sections to the top and bottom brackets.
Rollers
Ever wonder how your garage door glides effortlessly along the tracks? Rollers help. These small wheels are attached to the hinges and roll along the tracks, guiding the door’s movement.
You’ll typically encounter two main types of rollers:
- Nylon rollers: Quieter and more durable than steel rollers, offering a smoother operation.
- Steel rollers: More affordable but can be noisier and prone to wear and tear over time.
The type and quality of your rollers can significantly impact your garage door’s noise level and longevity.
Tracks
Tracks are the pathways that guide the rollers and the entire door during operation. They come in two varieties:
- Vertical tracks: Guide the door as it moves up and down.
- Horizontal tracks: Support the door when it’s fully open.
Properly aligned and maintained tracks are essential for smooth, safe, and quiet garage door operation. Bent or obstructed tracks can lead to jerky movements, excessive noise, and even damage to the door or opener.
3. Springs
Imagine trying to lift a several hundred-pound garage door with your bare hands! That’s where springs come in. They counterbalance the door’s weight, making it surprisingly light and manageable. Without adequately functioning springs, your garage door opener would struggle, and you’d feel the strain.
Torsion springs
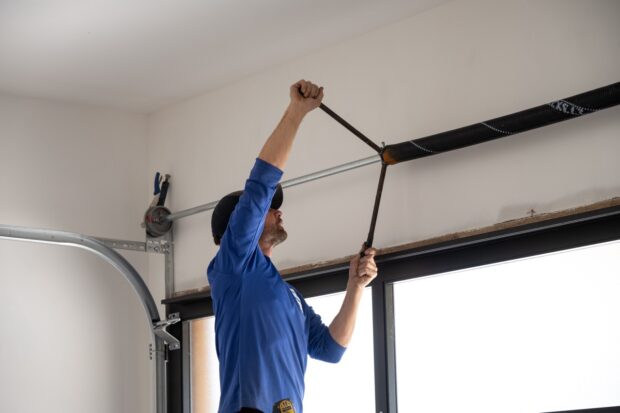

These tightly wound springs are typically located above the garage door opening, mounted on a metal shaft. As the door closes, the springs wind up, storing energy. When you open the door, that stored energy is released, helping to lift the door easily.
Safety Note: Torsion springs are under immense tension and can cause serious injury if handled improperly. Always leave adjustments and repairs to qualified garage door professionals.
Extension springs

Unlike torsion springs, extension springs are on either side of the door, parallel to the horizontal tracks. They stretch and contract as the door moves, providing the necessary counterbalance force. While generally safer than torsion springs, it’s still crucial to exercise caution and leave any maintenance or repairs to the pros.
Torsion vs. Extension Springs
Feature Torsion Springs Extension Springs Location Above the garage door opening On either side of the door Mechanism Wind and unwind to store and release energy Stretch and contract to provide counterbalance Lifespan Longer lifespan (typically 10,000 - 20,000 cycles) Shorter lifespan (typically 5,000 - 10,000 cycles) Safety Generally safer if they break, as they are contained Can be dangerous if they break, potentially becoming projectiles Noise Level Quieter operation Can be noisier, especially with lower-quality rollers Maintenance Require less frequent maintenance May require more frequent adjustments Cost More expensive initially Less expensive initially Space Requirements Require headroom above the door opening Suitable for low headroom situations Appearance More discreet, hidden above the door Visible on the sides of the door
Understanding the role of your garage door springs is essential for safety and proper operation. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prevent unexpected failures and ensure the longevity of your garage door system.
4. Garage Door Opener

Think of your garage door opener as the command center of the whole system. It provides the power and control necessary to automate the movement of your garage door. But it’s not just about convenience; a good opener also incorporates important safety features.
Motor
The motor is the heart of your garage door opener, providing the muscle to lift and lower the door. You’ll find different types of motors, each with its own characteristics:
- Chain drive: These are the most common and affordable type, but they can be noisy due to the metal chain that moves the trolley.
- Belt drive: Known for their quiet operation, belt drive openers use a rubber belt instead of a chain. They tend to be more expensive but offer a smoother and quieter experience.
- Screw drive: These openers use a threaded steel rod to move the trolley. They’re generally reliable and require less maintenance than chain drives, but they can be noisy in colder climates.
Choosing the right motor depends on your budget, your sensitivity to noise, and the frequency of use.
Safety Sensors
Safety is paramount when it comes to garage doors. That’s where photo eyes, or safety sensors, come in. These small devices are mounted near the bottom of the garage door tracks on either side. They emit an invisible beam of infrared light, and if that beam is broken (by a person, pet, or object), the door will stop closing and reverse direction. This crucial safety feature helps prevent accidents and injuries.
Remote Control
No more getting out of your car in the rain or fumbling for keys in the dark! Your garage door opener comes with a remote control that allows you to operate the door from the comfort of your vehicle or anywhere within range.
Modern remotes often include features like rolling code technology for enhanced security, preventing unauthorized access to your garage. You can also typically program multiple remotes to accommodate different family members or vehicles.
Other Essential Components
We’ve covered the major players in your garage door system, but a few more supporting components deserve your attention. These often-overlooked parts are crucial in keeping your garage door operating smoothly, safely, and efficiently. Let’s take a closer look.
Weatherstripping
Think of weatherstripping as the guardian against the elements. This flexible seal is typically found along the bottom and sides of your garage door, closing the gap between the door and the frame. It helps keep out rain, snow, wind, and even those pesky drafts.
Weatherstripping also helps to:
- Improve energy efficiency: By preventing heat loss in the winter and cool air escape in the summer.
- Reduce noise: It acts as a sound barrier, muffling outside noises.
- Prevent pests: Keeps unwanted critters from entering your garage.
Over time, weatherstripping can become brittle or damaged, so it’s important to inspect it periodically and replace it as needed.
Cables and Drums
Remember those powerful springs we talked about earlier? Well, cables and drums are their trusty sidekicks.
- Cables: These strong steel cables attach to the bottom corners of the garage door and run up to the drums. They help to safely control the movement of the door as the springs extend and retract.
- Drums: Mounted at the ends of the torsion spring shaft, drums wind and unwind the cables, ensuring a controlled and balanced movement of the door.
Cables and drums are critical safety components. If a spring breaks, the cables help prevent the door from crashing down, while the drums help to contain the broken spring.
Locks and Handles
While most of us rely on our garage door openers these days, it’s important to remember the good old-fashioned manual operation.
- Locks: Many garage doors are equipped with manual locking mechanisms that can be engaged for added security when you’re away for an extended period or if your opener malfunctions.
- Emergency release handle: This handle, usually a red cord hanging from the opener trolley, allows you to disconnect the door from the opener in case of a power outage or emergency. This lets you manually open and close the door.
Garage Door Struts
Ever noticed those horizontal reinforcements across the inside of your garage door? Those are struts that provide essential structural support to the door panels. They help prevent sagging and bending, especially for wider or heavier doors. Struts also contribute to your garage door’s overall stability and wind resistance.
Garage Door Jambs
The jambs are the vertical framing members that surround the garage door opening. They provide a sturdy framework for the door to operate within and help seal the opening when it is closed. The jambs also attach the tracks and weatherstripping. Proper installation and maintenance of the jambs are crucial for your garage door’s smooth and secure operation.
Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of these manual components. They can come in handy when you least expect it!
Ready to take control of your garage door?
Feeling overwhelmed by all these garage door parts? Don’t worry; Doorvana is here to help!
Whether you need a simple repair, a complete system overhaul, or expert advice, our team of experienced technicians is ready to assist you. We offer a wide range of services, including:
- Garage door repair and maintenance
- Spring replacement
- Opener installation and repair
- Hardware upgrades
- And much more!
Don’t let a faulty garage door disrupt your life. Contact Doorvana today for a free consultation, and let us handle all your garage door needs. We’re committed to providing reliable, affordable, and professional service that you can count on.
Call us now or visit our website to schedule your appointment!
Conclusion
Understanding the various parts of your garage door empowers you to maintain it better, troubleshoot issues, and ensure its longevity. By familiarizing yourself with the components discussed in this guide, you can make informed decisions about repairs, upgrades, and preventative maintenance. Remember, regular inspections and timely service can save you from costly repairs and ensure your garage door’s safe and reliable operation for years. If you’re unsure about handling any aspect of your garage door, don’t hesitate to contact a qualified professional for assistance.
FAQs about garage door parts
What are the most important parts of a garage door?
While all parts play a role, the most crucial are the springs (torsion or extension), which counterbalance the door’s weight, and the opener, which provides the power to lift and lower it. Don’t forget the safety sensors (photo eyes) that prevent accidents!
How often should I lubricate my garage door?
It’s generally recommended that you lubricate the moving parts of your garage door (hinges, rollers, tracks) every 3-6 months. Use a garage door-specific lubricant, and avoid WD-40, as it can attract dust and debris.
Why is my garage door making a grinding noise?
A grinding noise could indicate several issues, including:
- Worn-out rollers: Replace them with nylon rollers for quieter operation.
- Dry or damaged hinges: Lubricate them or replace them if necessary.
- Track misalignment: Check for bends or obstructions in the tracks.
- Opener problems: The motor or drive mechanism may need attention.
It’s best to call a professional technician to diagnose the problem if unsure.
What should I do if my garage door spring breaks?
Do not attempt to fix it yourself! Broken garage door springs are hazardous and can cause serious injury. Call a qualified garage door technician immediately for a replacement.
How can I improve the energy efficiency of my garage door?
Consider these options:
- Insulated door sections: Choose a door with a higher R-value for better insulation.
- Weatherstripping: Ensure the weatherstripping around the door is in good condition to seal gaps.
- Garage door threshold: Install a threshold to seal the gap at the bottom of the door.
Can I replace my garage door opener myself?
While possible, hiring a professional for garage door opener installation is generally recommended. They have the expertise to ensure proper installation, balance the door, and connect the safety features correctly.